How to Write a Dissertation in College
This long piece of academic writing has the purpose of describing your unique research. It is called a dissertation or, very often, has the name of a thesis. The assignment is usually required for obtaining a Ph.D. or Master's degree or, sometimes, Bachelor’s degree.
Since this paper is rather long, you should know for sure where to start and how to comply with all the requirements properly. We are going to provide essential information about the structure and writing process in this article.
Making Up the Structure
The structure of your dissertation will depend on many factors. They are a topic, subject, or field of study, your institution’s location, as well as the approaches and methods you use.
For instance, if you are supposed to write a dissertation on humanities, make it in the form of a long essay, with the main argument meant to support a thesis statement. The chapters will reveal the important themes and case studies as well.
However, for your practical research in sciences or social sciences, choose the structure that will include all the elements described below. Each of them can become a unique chapter or a combination of some structural parts. For example, you can place discussion and research results in one chapter.
You may need to change the order of sections as well, depending on the field of study and your university’s requirements. You should always check the guidelines and discuss the structure with your professor.
How to Write a Title Page
This first page of your work needs a title of the dissertation, your full name, the name of your department and university, the program the paper is written for, and, if required, the institution’s logo. You should also indicate the submission date, your supervisor’s name, and, in some cases, your student’s number.
Be aware of the requirements for formatting. In some institutions, they can be rather strict.
Acknowledgement Section
As a rule, this part is optional. Here, you can thank your helpers, colleagues, and supervisors for contributing to your paper. You can also include your friends and family to express your gratitude for their support.
If you have conducted an empirical experiment and worked with a team, you may also thank them.
Abstract
This is a summary of your dissertation written concisely. It can be about 150-350 words and include:
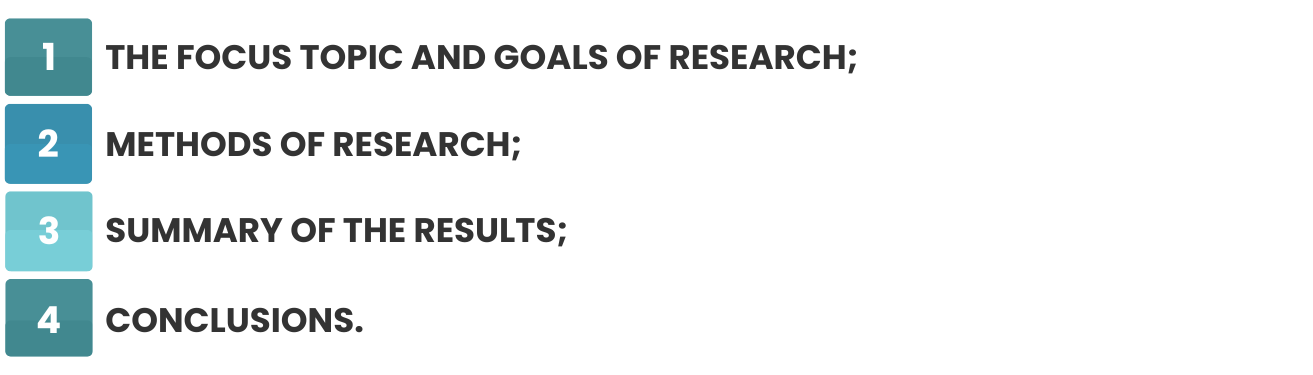
The abstract is usually written after completing the paper when you have already seen what everything was about.
An abstract is the first thing people will read about your dissertation, so it should be straightforward and strong.
Table of Contents
This page will provide the overall idea of your paper to its readers. You should make a clear list of all chapters with their subheadings. Everybody who opens your document should see how to navigate it.
Include all the parts of your work in the table of contents (together with appendices).
Figures and Tables
Such a list is needed when you have used a lot of tables or figures in your academic paper. Make a numbered list for more convenience.
Abbreviations
These should also be enlisted. Compose this list in alphabetical order. It makes it easier for readers to look up some abbreviations they are unsure about.
Glossary
If your dissertation requires a lot of specialized terms, not all of them are quite familiar to readers. That is why you need to make up a glossary. Place all the terms in alphabetical order and give a clear explanation, definition, or description of them.
How to Write an Introduction
Here, you should point out the purpose and topics of your research, indicating their relevance and topicality. Describe in short what your dissertation is going to be about. The introduction should contain:

Everything you include in the introduction should be clear and engaging for readers.
Literature Review
This is also the basis for your theoretical framework. You need it to express your understanding of which academic papers exist on this topic. As a rule, you make this review while beginning to research the problem. To compose this part, you need to:
- collect sources and choose the most appropriate of them;
- evaluate and analyze each source critically;
- make an overall idea based on connections between all the chosen sources.
The clear structure of your paper based on the sources used should involve:
- addressing the gaps in the existing research;
- taking up new approaches to the topic;
- putting forward appropriate solutions;
- continuing debate on theoretical approaches;
- complementing the existing knowledge with new information.
The theoretical framework is a wider notion that provides the basis for your research. It involves key theories and concepts. This part should answer the research questions and define relationships between main concepts and variables.
Methodology
This chapter describes the process of your research. Based on this, your reader will make conclusions about your work’s validity. The section includes:

Report all the details consistently and accurately to persuade your reader that you have chosen the optimal methods and approaches to meet all the objectives successfully.
How to Represent the Results
This chapter should highlight all the questions and answers obtained from the research, extend themes and hypotheses if there were any. This section can be written separately from the discussion part or be combined with it.
Usually, the results are represented solely when you have done experimental or quantitative research. To do that, you need to:
- provide relevant statistics - both descriptive and inferential ones;
- determine how the obtained results correspond to the questions and hypotheses;
- present figures and tables to support your results and show them clearly to readers;
- give information about all relevant results, even those which have not supported your hypotheses or initial ideas;
- never include any speculations, subjective considerations, or interpretations.
All the extra information that supports the results (such as transcripts of interviews, the content of questionnaires, or raw numbers) can be presented in appendices.
Discussion
Here, you go more deeply into the implications and meanings of your research results. Discuss whether you have received what you expected if they follow the exact framework represented in previous chapters and whether there has been something completely unexpected. You may need to:
- interpret what the obtained results mean;
- explain why the results are important;
- discuss the limitations or what cannot be obtained from your research.
Explain in detail why some results turned out to be unexpected or give alternative interpretations of them. You can also use the relevant sources to back up these interpretations.
Conclusion
This part should answer the research question of your dissertation. Your readers should be sure that all the arguments and focused points are provided and supported properly, and that your research has contributed a lot to them.
Sometimes, you may need to include a short section or paragraph before the conclusion section to inform briefly about the main outcomes and then interpret and discuss them in more detail.
As a rule, the conclusion is a final section of your paper where you summarize your dissertation and provide an overall reflection on every finding of your research. The conclusion may also include some recommendations for future research. You should also explain to your reader why your research is vital for the development of the field, and what new points it has added to it.
Making Up the Reference List
Here, you give a complete list of all your sources with appropriate details. Sometimes, this part is called a bibliography or works cited according to the citation style required. The most widely used styles are MLA and APA. So, check all the requirements for formatting. You can discuss the unclear points with your supervisor. You can also use our online Citation Generator for the format required to save your time.
What Appendices Can Include
All the information included in your dissertation answers the research questions and contributes to the goals and objectives of your paper. To support this information, you may need to include some additional data, graphs, visuals, or charts. You may also need to support your findings with some documents (e.g., survey questions or interview transcripts). All these pieces can be added to appendices.
Final Thoughts
Now, you know what the main structural parts of your dissertation are and how to write them. You need to be sure that all these solutions are in their appropriate places. You should also check whether your paper does not contain any style, grammar, or spelling mistakes. That is why proofreading and editing should also be an essential part of your work. Formatting errors should also be detected and corrected thoroughly.
The quality of all work and its final assessment can depend significantly on these processes, so you or any professional paper writer should not ignore or skip them. You may need to make up one or two draft papers to focus on inconsistencies. Or you may need a professional service for editing your dissertation. In any case, the results of your work will be great if you pay attention to this finalizing process.
