Editing and Proofreading Tips for Everyone
Proofreading is reading the final draft of any text and looking for mistakes in it to fix them. At this final stage, minor spelling and punctuation mistakes and formatting issues are fixed. It is crucial for any text that will be shared with an audience.
Table of contents
Editing vs proofreadings
These are different steps of the revising process. Editing typically means you make major changes in content, language, and structure, while proofreading involves fixing minor errors. Usually, a text goes through several editing levels. Here are the most common steps in this process.

Here is more detailed information:
| Type of editing | What it involves |
|---|---|
| Content editing | Revising the first draft for the first time, making significant alterations in the content, moving, adding, or excluding entire sections. |
| Line editing | Revising the use of language. It usually involves rewriting specific parts and changing the structure of paragraphs. |
| Copy editing | Bringing individual sentences to perfection to provide correct grammar, clear syntax, and stylistic consistency. |
| Proofreading | Checking for any remaining errors, such as misspelled words, misplaced punctuation, etc. At this stage, formatting is also checked. |
In the traditional publishing process, different professionals are responsible for each specific stage of revision. In other instances, there is usually more overlap between the steps. Many services unite some steps into a single one, where grammar, syntax, and style are addressed simultaneously with minor spelling and punctuation mistakes.
Editing
Usually, editing is done on several levels:
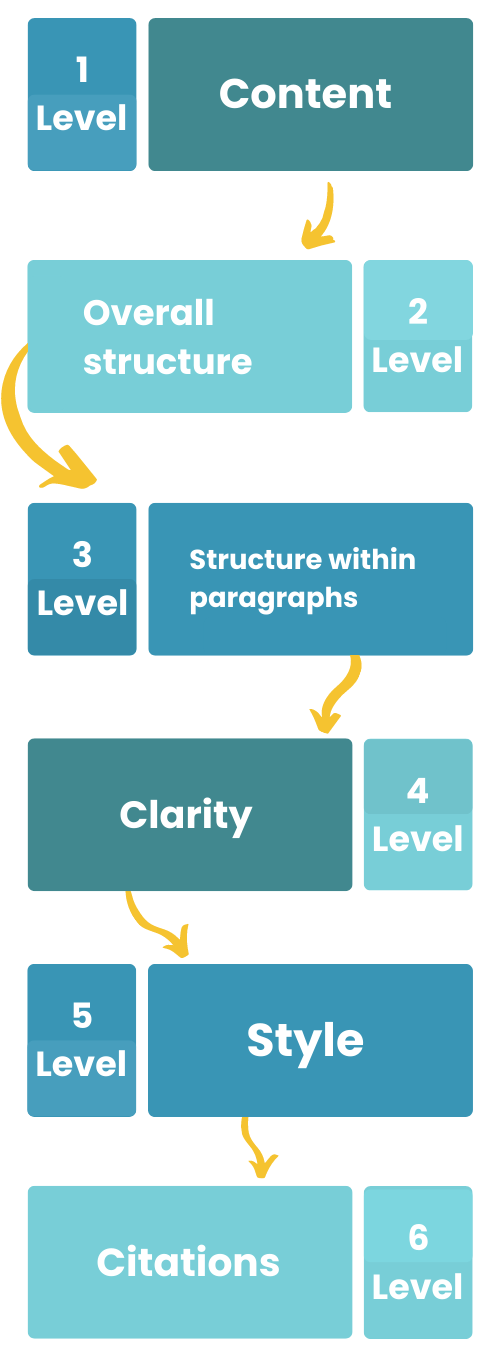
Let's take a closer look at each of them.
Content
Here are the main points to check at this level:
- Have you done everything the assignment requires?
- Is your argument complete?
- Are all the claims consistent?
- Are all points supported with strong evidence?
- Is all the information in the writing piece relevant to the assignment?
Overall structure
At this stage, check if:
- The paper has n appropriate introductory and concluding part.
- The thesis is clearly stated at the very beginning of the paper.
- Each body paragraph is clearly related to the thesis.
- All the paragraphs come in a logical sequence.
- There are clear transitions between paragraphs.
Structure within paragraphs
When editing at this level, check if:
- Each paragraph has a topic sentence.
- Each paragraph sticks to one major idea.
- There are no extraneous or missing sentences in your text.
Clarity
Once you have moved to this step, check these points:
- All the important terms are defined.
- The meaning of each sentence is clear and obvious.
- It is clear what each pronoun refers to.
- The words are chosen appropriately to express every thought.
Style
Editing at this level involves checking the following:
- An appropriate tone is used.
- A proper gendered language is used.
- The sentences have appropriate length and clear structure.
- There is no wordiness in the text.
Citations
At this stage of editing, check if you have appropriately cited quotes, paraphrases, and ideas from the sources. Make sure they are formatted according to the requirements.
While editing at all these levels, you will likely make significant changes in the content of the writing piece. Keep an eye out for patterns of the most often made mistakes. It is helpful to know what kinds of problems you tend to have, especially when editing a large paper. By having identified a pattern, it is easier to develop techniques for avoiding and correcting future instances of that pattern.
Proofreading
Basic proofreading skills are crucial for any essay writer. You will need them for emails, business reports, blogs, and academic papers. Here are some tips that will help you proofread more effectively.
Start with editing
Before you begin proofreading, carefully revise and edit the text. It makes no sense to fix minor errors if you might later rewrite paragraphs or delete whole sections. Proceed to proofreading only after completing a final draft that you are satisfied with.
Put the text aside for some time
After reading the same text for hours and even days, it becomes much more complicated to notice mistakes. So set this work aside for a day or two, or at least for an hour, so that you can take a fresh look at it later.
Proofread a printed copy
Reading the text on a printed page is one more useful tip to use for noticing things that might have escaped your attention on the screen. Besides, printing the writing piece out is a good chance to check whether the formatting is correct and consistent on the page.
Use digital shortcuts
Word processing software will help you fix multiple mistakes efficiently. Obviously, run a spell check — but do not entirely rely on such programs. They have a limited dictionary, so some words that show up as misspelled may actually just not be in their memory. Additionally, they cannot catch misspellings that form another valid word. For example, if you type "you're" instead of "your," or "to" instead of "too," the spell checker will not catch the error.
If you notice that you repeatedly misspell a particular word, consider using the Find and Replace function to fix the mistake throughout the document. But do not use "replace all." Instead, click through and check every replacement.
Have a list of what to look for
This will help you manage your time better and avoid feeling overwhelmed. For example, consider using the table below.
| Spelling and word choice confusions |
|
| Misplaced punctuation |
|
| Stylistic inconsistency |
|
| Formatting issues |
|
Read from the end
Read separate sentences starting from the end of the text. This will help you concentrate on the sentence itself rather than on the ideas of the paper as a whole.
We hope that with these editing and proofreading tips, it will be much easier for you to bring your writing pieces to perfection.
